Morton’s Metatarsalgia
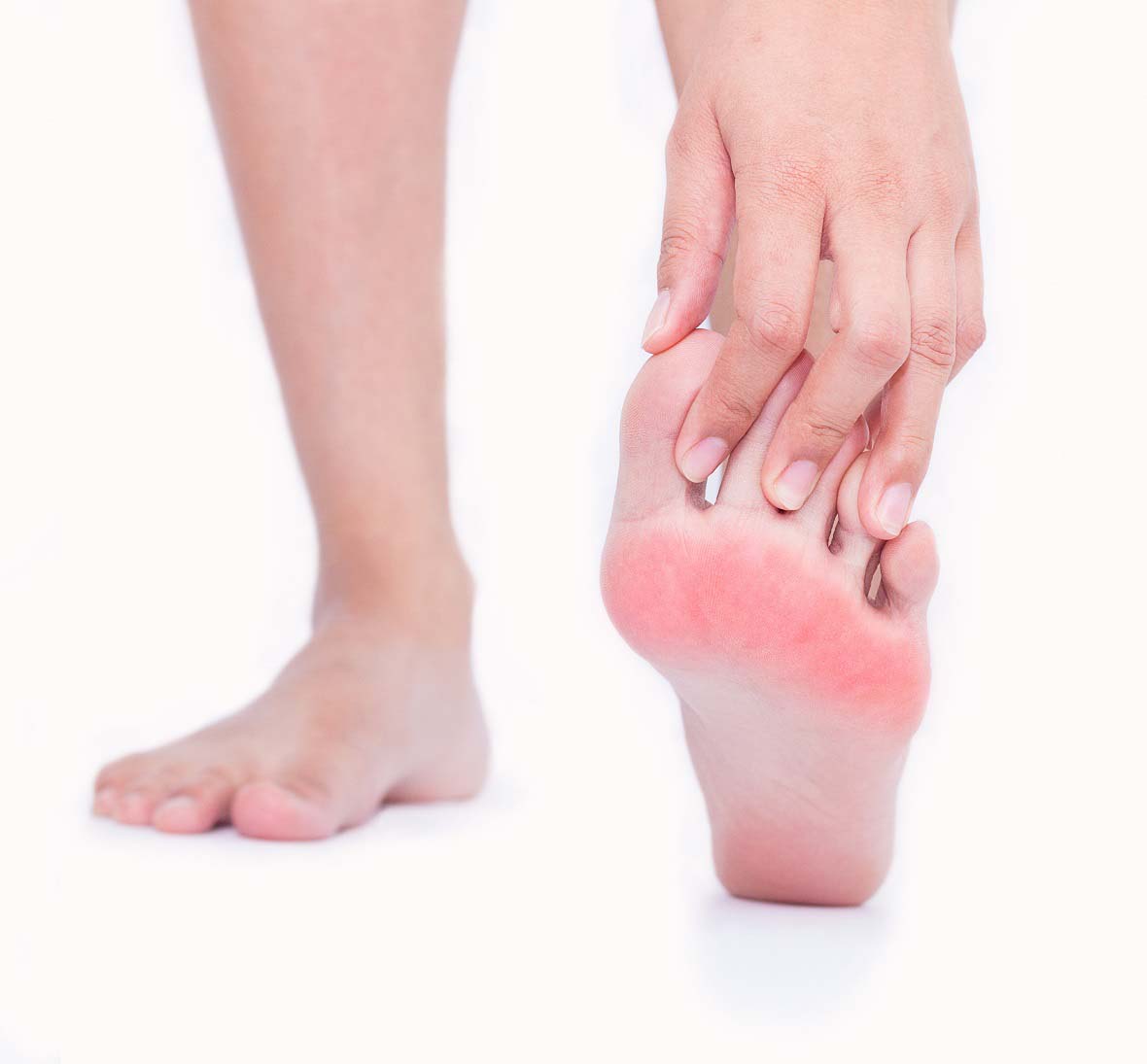
We call “Morton’s Metatarsalgia” to the pain located in the front of the feet, that is, in the area corresponding to the metatarsal support and fingers.
It is not, therefore, a disease, but a broad syndrome that can be caused by multiple causes. Morton’s Metatarsalgia is a well-known condition within disorders that affect the foot. It is an entity known by Civinnini in 1835 and by Durlacher in 1845 that the definition as a neuralgic condition of the forefoot with involvement of the plantar nerve; Later Thomas Morton in 1876, returned the description of Durlacher under the term of “painful affection of the 4th metatarsophalangeal joint”.
The term Neuroma, which is usually associated with this condition, was first used in 1940 by Betts, author who clearly demonstrated the relationship between metatarsalgia and the presence of nervous swelling and, above all, the healing of Patients by cleavage of this “neuroma”. In fact, it is not a nerve tumor itself, but a pseudoneuroma.
It is important to emphasize their predominance in the female sex (in a proportion of 85, 5%). First of all the acute pain that is seen, however, the night sea, is to look for this disease; This pain can be paroxysmal, of very intense electric shock type, although it can be continuous and be influenced by the gait and that very often it calms when taking off the shoes. In the exploration, great importance attaches to the vertical pressure of the metatarsal intercapital space that triggers the pain, which can be flashing; This pressure must enter the two metatarsal heads located on both sides of the affected space and not in the vertical of the latter, therefore this pain different from that which appears in static metatarsalgias.
Morton’s Metatarsalgia diagnosis
The clinical diagnosis is quite easy, but there are doubts about whether an ultrasound can be performed and the whole case using a Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, having the techniques of 100% specification. Conservative treatment consists of infiltrations with self-rehabilitation exercises within 8 days after infiltration and foot tips: lower heels, wider anterior end, good quality insole. If this treatment is treated the surgical treatment has been indicated.
The resumption of gait is allowed from the day of surgery, and may be smoothed after the 15th to 20th postoperative day.
Within the surgical treatment ,we have since 1994, the endoscopic decompression of the space interdigital described by Barret, which consists of the decompression, neurolysis – release of the plantar nerve by the section of the deep intermetatarsal transverse ligament. This endoscopic decompression is effective in approximately 85% of cases when the indication is correct. In case of failure we have the classic technique of open resection of the neuroma, either by the plantar – dorsal approach.
The surgical techniques performed by Orthopedic surgeons and traumatologists, because of their stability, ease of fixation and versatility, offer patients early support and obtaining consolidation and recovery faster .
If you present this symptomatology do not wait more time and ask for consultation, since the passage of time will aggravate your problem.
Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology. Arthroscopic Surgery. Sports Traumatology.